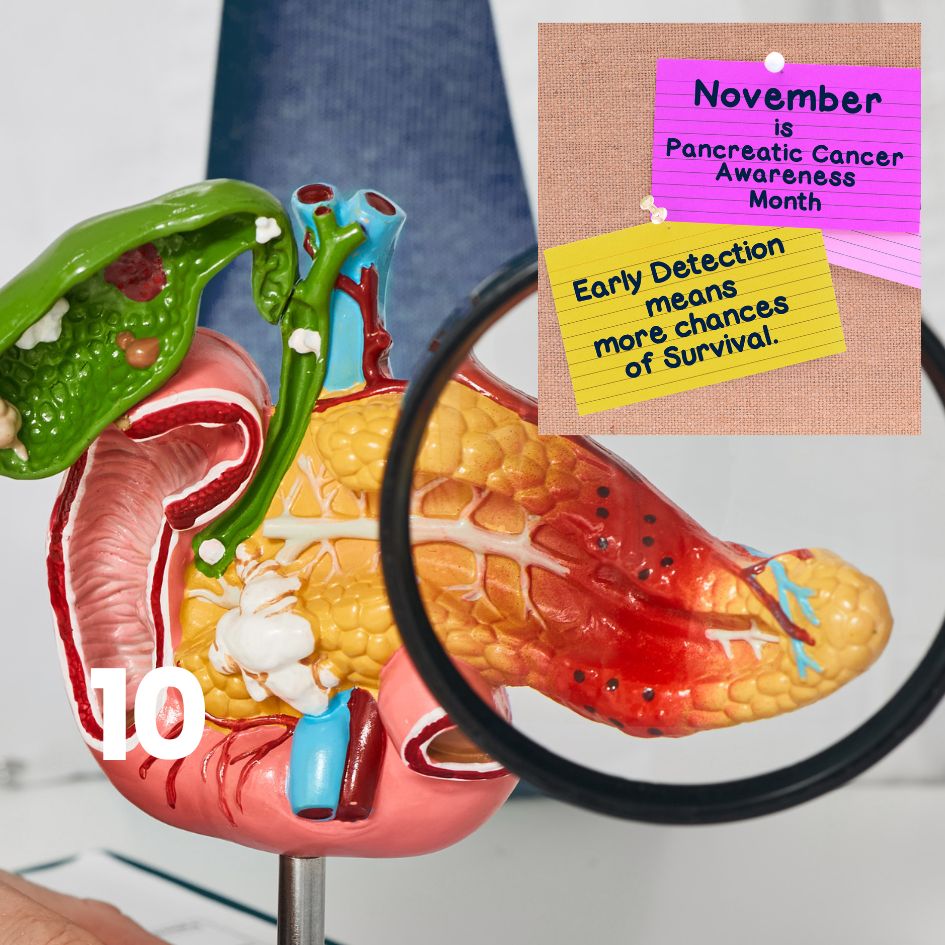
The pancreas, an organ involved in digestion and insulin production. Often asymptomatic in its early stages, pancreatic cancer frequently goes undetected until advanced stages, making early diagnosis
challenging. Common symptoms can include abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and changes in appetite. Prognosis is generally poor, with a five- year survival rate typically below 10%, largely due to late-stage diagnosis. Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation
therapy, but effectiveness varies based on the cancer’s stage and location.
10 important questions and answers that everyone must read to understand about the Pancreas and its cancer.
- What is the pancreas, and what role does it play in the body?
The pancreas is a glandular organ located behind the stomach. It plays a crucial role in digestion by producing digestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels.
- What are common pancreatic diseases?
Common pancreatic diseases include pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), diabetes (due to malfunctions in insulin production), and cystic fibrosis (which affects the pancreas' ability to produce digestive enzymes).
- What are the symptoms of pancreatitis?
Symptoms of pancreatitis can include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, rapid pulse, and a swollen abdomen. In chronic cases, it may also lead to weight loss and indigestion.
- What are the risk factors for pancreatic cancer?
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer include smoking, obesity, age (increased risk after age 45), diabetes, pancreatitis, and a family history of pancreatic cancer.
- How is pancreatitis diagnosed?
Pancreatitis is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests (looking for elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes), imaging tests (such as CT scans or ultrasounds), and sometimes endoscopic procedures.
- What lifestyle changes can help promote pancreatic health?
To promote pancreatic health, one should maintain a healthy diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains), avoid excessive alcohol consumption, stay hydrated, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular exercise is also beneficial.
- How does diabetes relate to the pancreas?
Diabetes, particularly Type 1 and Type 2, is closely related to the pancreas. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, while Type 2 diabetes is often linked to insulin resistance and can stem from pancreatic dysfunction.
- What are some diagnostic tests for pancreatic diseases?
Common diagnostic tests for pancreatic diseases may include blood tests for enzyme levels, imaging tests (such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI), endoscopic ultrasounds, and biopsies to analyze suspicious tissue. - What is the prognosis for someone diagnosed with pancreatic cancer?
The prognosis for pancreatic cancer can vary widely based on the stage at which it is diagnosed. Unfortunately, it has a low survival rate because it is often detected in advanced stages. Early detection and treatment can improve outcomes.
- What support resources are available for individuals with pancreatic diseases?
Various resources are available online if you want to know in detail about pancreatic diseases, including the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network (PanCAN), the American Diabetes Association (ADA), WebMD.
- Conclusion
Remain aware about your pancreatic health, understand the signs and symptoms of related diseases, and follow healthy lifestyle choices. It can contribute to better overall health and early intervention for pancreatic conditions.